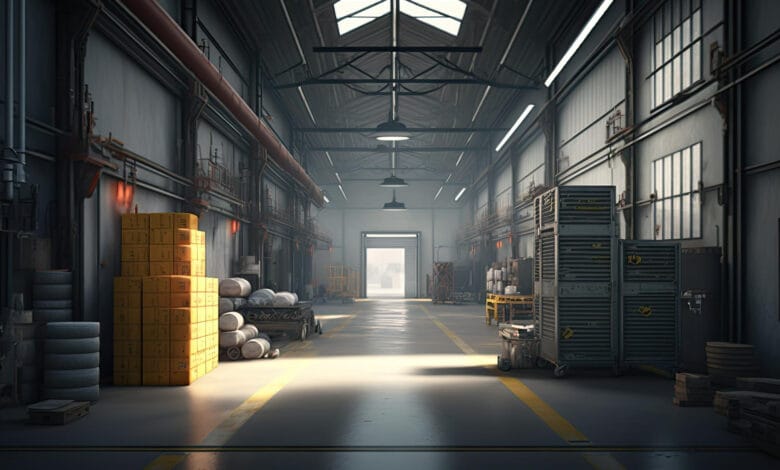
The Industrial Architecture 19th Century marked a revolutionary era in building design, redefining urbanism. With the rapid developments of the Industrial Revolution, architecture shifted from handmade structures to machine-produced materials, giving rise to large-scale factories, warehouses, and transport hubs. This period introduced new construction methods that laid the foundation for contemporary industrial design.
In this article, we will study the history, and characteristics of Industrial Architecture, including its influence across the world, and how it shaped modern architecture.
What is Industrial Architecture?
The Industrial Architecture 19th Century emerged as a response to rapid urbanization and technological innovations. This architectural style focused on efficiency, strength, and scale, and used industry-inspired materials like iron, steel, and glass to create massive structures. Unlike earlier ages that emphasized highly decorative features, industrial buildings were designed with a focus on form and function.
The rise of Industrial Revolution architecture introduced the construction of large factories, mills, and rail stations. These spacious buildings featured open floor plans with high ceilings to accommodate the growing workforce.
Innovations in Building Materials and Techniques
During this time, engineers and architects experimented with new materials to improve structural strength. Iron and steel made the construction of 19th-century industrial buildings possible, creating taller, more resilient structures. The use of prefabricated parts simplified the construction process, saving cost and time.
Furthermore, advanced ventilation systems and fireproofing techniques improved workplace safety. Architects designed innovative layouts that maximized workflow, leading to the development of vast factory complexes that defined the urban fabric of industrial cities.
The Industrial Revolution and Its Influence on Architecture
Urban Expansion and the Changing City
The Industrial Revolution reformed cityscapes worldwide, turning small towns into major industrial hubs. As factories and mills multiplied, new housing developments were built to accommodate workers, leading to the rise of densely populated urban centers. This growth called for architects to rethink conventional building practices, resulting in the emergence of Industrial-era architectural styles that combined function with mass production.
Skylines became dominated by chimneys, warehouses, and iron-framed buildings, reflecting the era’s commitment to progress and efficiency. Transportation infrastructure, such as railways and bridges, improved significantly, supporting the fast movement of goods and people across regions.
Impact on Labor and Social Structures
The growth of factories drastically changed labor conditions. Factory layouts prioritize productivity, with assembly lines and mechanized production replacing traditional artisanal methods. While this improved employee output, it also led to overcrowded, hazardous work environments.
The demand for better living and working conditions eventually influenced architectural reform, leading to improved airflow, lighting, and sanitation in industrial buildings. These early changes paved the way for modern workplace safety standards and sustainable architectural practices.
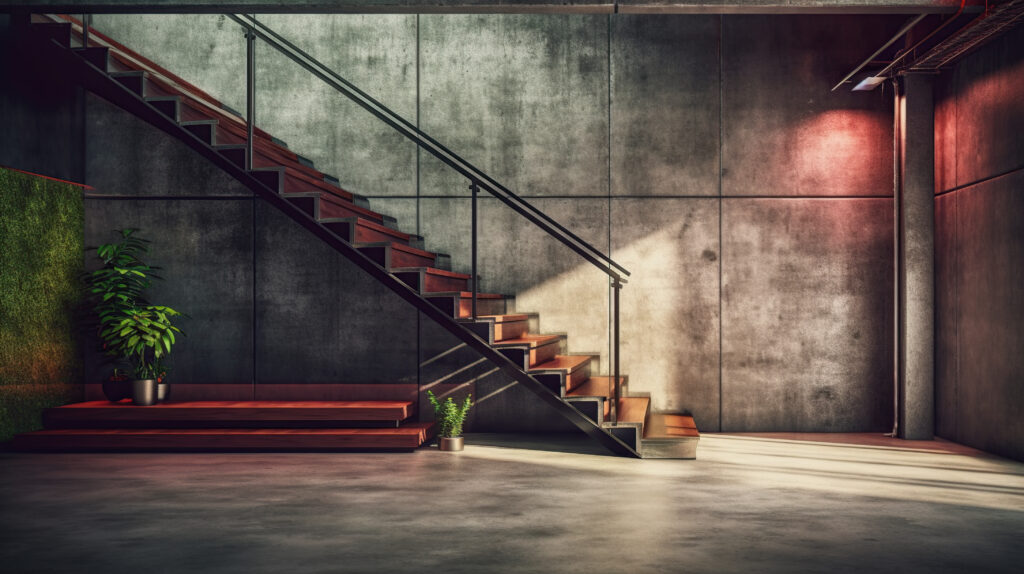

Elements of Industrial Architecture 19th Century
The Industrial Architecture 19th Century has several features that set the buildings apart from old-age architectural styles.
1. Open Spaces
Industrial buildings featured high ceilings and open floor plans to accommodate machinery and large workforces. This floor plan layout improved air circulation and made operations more efficient.
2. Minimalism
Unlike earlier styles, industrial styles focused on simplicity. Buildings were designed for function over decoration, reflecting the efficiency-driven mindset of the Industrial Revolution architecture.
3. Exposed Materials
A signature element of industrial design is the use of steel beams, exposed brick, and concrete floors. Plumbing, ductwork, and exposed wiring were often left visible, for a more raw and rustic vibe.
4. Abundant Natural Light
Floor-to-ceiling metal-grid windows and skylights were installed to flood spaces with maximum natural light and reduce reliance on artificial lighting.
These elements made Industrial Architecture highly durable, efficient, and influential in modern industrial-style designs.
The introduction of historic industrial architecture in the USA could be seen when cities like Chicago and New York became home to huge industrial developments, featuring multi-story warehouses and early-age skyscrapers that set the stage for modern commercial design trends.
Industrial Architecture in Europe and the USA
While Europe pioneered early Industrial Architecture 19th Century, the United States quickly implemented and expanded upon these ideas. European industrial hubs, such as Manchester and Berlin, were known for their large brick factories and iron-framed bridges, while American cities integrated steel-framed towers and large-scale production facilities.
Famous Examples of Industrial Architecture
Many iconic industrial buildings dating from the 19th century still stand today, now as monuments. Examples include:
- The Crystal Palace (UK) – Among the first examples of prefabricated construction using iron and glass.
- Pullman Factory (USA) – A ground-breaking industrial complex designed to support both manufacturing and worker housing.
- Alfred Mylne’s Warehouse (Germany) – A model of effective industrial design with reinforced steel structures.
These buildings highlight the adaptability and resilience of industrial architecture, influencing modern urban design.
The Legacy of 19th-Century Industrial Design
Modern Modifications and Sustainability
Many industrial buildings have been repurposed into lofts, offices, and cultural centers. The adaptive reuse of industrial structures preserves their historical integrity while including sustainable design elements. This trend has led to a resurgence of interest in this design style, as architects and developers combine vintage with contemporary.
The Future of Industrial Architecture
Today, the principles of Industrial Architecture continue to inspire contemporary design. The use of steel, exposed brick, and open layouts is still popular in urban developments. Sustainable approaches, such as passive cooling and energy-saving lighting, further strengthen the legacy of 19th-century industrial innovations.
Conclusion
The Industrial Architecture 19th Century played an important role in changing modern urban cityscapes, introducing revolutionary materials and construction methods that transformed design. From the towering factories of Industrial architecture to the 19th-century buildings, this era left a lasting impact on the architectural world. Modern industrial designs and adaptive reuse projects help the industrial legacy to live on today. By preserving these historical structures and integrating green innovations, architects continue to celebrate the ingenuity of the past while building for the future.
Source: Architizer